B2B Mastery: 7 Powerful Strategies to Skyrocket Your Business Growth
If you’ve ever wondered how companies sell to other companies, you’re diving into the world of B2B. It’s not just about transactions—it’s about relationships, strategy, and long-term value that fuels global economies.
What Exactly Is B2B and Why It Dominates Global Commerce

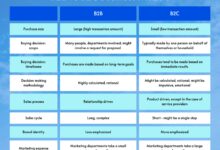
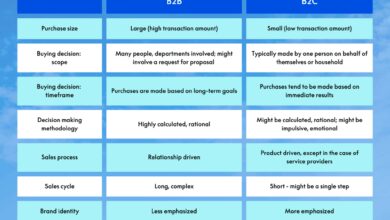
Business-to-business (B2B) refers to transactions between companies, such as a manufacturer selling to a wholesaler or a software provider offering tools to enterprises. Unlike B2C (business-to-consumer), B2B focuses on solving business problems, not just fulfilling personal needs.
The Core Definition of B2B
B2B, or business-to-business, describes commerce where one company provides products or services to another. This can include raw materials, software platforms, consulting services, logistics, and more. The key differentiator from B2C is the decision-making process—B2B sales often involve multiple stakeholders, longer sales cycles, and higher transaction values.
- B2B transactions are typically based on contracts and long-term agreements.
- Examples include Salesforce selling CRM software to enterprises or Intel supplying chips to computer manufacturers.
- The focus is on efficiency, ROI, and scalability rather than emotional appeal.
“B2B is not just about selling; it’s about solving complex business challenges with strategic partnerships.” — Forbes Insights
How B2B Differs from B2C
While both B2B and B2C involve selling, their dynamics differ significantly. In B2C, decisions are often impulsive and driven by emotion, branding, and convenience. In contrast, B2B buyers prioritize logic, cost-benefit analysis, and long-term value.
- Sales cycles in B2B can last weeks or months, compared to minutes or hours in B2C.
- B2B marketing emphasizes thought leadership, case studies, and whitepapers, while B2C leans on ads, influencers, and promotions.
- Pricing in B2B is often customized and negotiated, whereas B2C prices are usually fixed.
Understanding these differences is crucial for crafting effective marketing and sales strategies. For deeper insights, check out Investopedia’s comprehensive guide on B2B.
The Evolution of B2B: From Trade Shows to Digital Marketplaces
The B2B landscape has undergone a dramatic transformation over the past few decades. What once relied heavily on face-to-face meetings and printed catalogs now thrives in digital ecosystems powered by AI, data analytics, and e-commerce platforms.
Historical Roots of B2B Commerce
B2B has existed as long as businesses have. In the early 20th century, industrial suppliers used trade journals and direct mail to reach potential clients. Trade shows were the primary venue for networking and deal-making. Relationships were built over handshakes and long lunches.
- Pre-internet B2B relied on phone calls, faxes, and physical catalogs.
- Procurement was manual, slow, and often localized.
- Trust and personal relationships were the foundation of every deal.
Despite the lack of technology, these methods laid the groundwork for modern B2B practices—relationship-building remains a cornerstone today.
The Digital Revolution in B2B
The rise of the internet in the 1990s marked a turning point. Companies began creating websites to showcase products, and email became a standard communication tool. By the 2000s, e-procurement systems and online marketplaces like Alibaba emerged, streamlining global supply chains.
- Platforms like LinkedIn revolutionized B2B networking and lead generation.
- CRM systems like HubSpot and Salesforce enabled better customer tracking and engagement.
- E-commerce portals allowed businesses to buy and sell 24/7 without intermediaries.
Today, over 70% of B2B buyers prefer to research and purchase online, according to a McKinsey report. This shift has forced companies to rethink their sales models and digital presence.
B2B Business Models: Understanding the Key Types
Not all B2B companies operate the same way. There are several distinct B2B business models, each with its own revenue structure, customer base, and operational focus. Understanding these models helps businesses identify their niche and optimize their strategy.
Manufacturers and Wholesalers
This traditional B2B model involves companies that produce goods and sell them in bulk to distributors or retailers. For example, a steel manufacturer sells to construction firms, or a pharmaceutical company supplies drugs to hospitals.
- High-volume, low-margin sales are common.
- Logistics and supply chain management are critical.
- Long-term contracts ensure stability and predictability.
Efficiency and scalability are key success factors. Companies like 3M and Caterpillar exemplify this model, serving industries ranging from healthcare to infrastructure.
Software as a Service (SaaS) Providers
SaaS has become one of the fastest-growing B2B sectors. These companies offer cloud-based software solutions on a subscription basis, such as project management tools, customer relationship management (CRM) systems, or cybersecurity platforms.
- Recurring revenue models provide predictable income streams.
- Customer success and onboarding are crucial for retention.
- Scalability allows rapid growth with minimal incremental cost.
Examples include Slack, Zoom, and Adobe Creative Cloud for enterprise. According to Gartner, global public cloud spending will reach $678.9 billion in 2024, with SaaS being the largest segment.
Service-Based B2B Companies
These firms offer expertise rather than physical products. Consulting agencies, marketing firms, legal services, and IT support fall under this category. Their value lies in knowledge, experience, and problem-solving.
- Revenue is often project-based or retainer-driven.
- Client relationships are deeply personalized.
- Brand reputation and case studies are powerful marketing tools.
Firms like Deloitte, Accenture, and McKinsey dominate this space, helping organizations navigate digital transformation, regulatory compliance, and strategic planning.
The B2B Sales Process: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
Selling in the B2B world is a complex, multi-stage process that requires precision, patience, and persistence. Unlike B2C, where a single customer might make a quick purchase, B2B sales involve multiple decision-makers, extensive research, and rigorous evaluation.
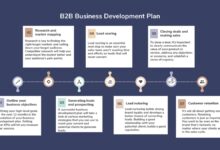
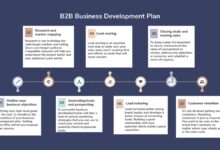
Lead Generation and Prospecting
The first step in any B2B sales cycle is identifying potential customers. This involves researching companies that could benefit from your product or service. Tools like LinkedIn Sales Navigator, ZoomInfo, and HubSpot are commonly used for lead discovery.
- Content marketing (blogs, webinars, eBooks) attracts inbound leads.
- Outbound strategies include cold emailing, calling, and social selling.
- Ideal Customer Profiles (ICPs) help focus efforts on high-potential accounts.
Effective prospecting isn’t about volume—it’s about relevance. A well-researched, personalized outreach message has a much higher conversion rate than generic spam.
Qualification and Needs Assessment
Not all leads are worth pursuing. The qualification stage determines whether a prospect has the budget, authority, need, and timeline (BANT framework) to make a purchase.
- Sales reps conduct discovery calls to understand pain points.
- Questions focus on current challenges, goals, and existing solutions.
- Tools like Gong or Chorus record and analyze sales conversations for insights.
This stage ensures that sales teams invest time only in viable opportunities, improving efficiency and close rates.
Presentation, Proposal, and Negotiation
Once a lead is qualified, the next step is presenting a tailored solution. This often involves a demo, a detailed proposal, and pricing discussions.
- Demos should highlight ROI and address specific business challenges.
- Proposals include scope of work, deliverables, timelines, and costs.
- Negotiation may involve discounts, extended trials, or custom features.
Transparency and flexibility are key. According to Capterra, 68% of B2B buyers expect vendors to customize their offerings.
Closing and Onboarding
Closing the deal is just the beginning. The onboarding process ensures the customer successfully adopts the product or service.
- Customer success teams guide implementation and training.
- Clear communication prevents misunderstandings and churn.
- Early wins build trust and set the stage for upselling.
A smooth onboarding experience can increase retention by up to 80%, making it a critical phase in the B2B lifecycle.
B2B Marketing Strategies That Deliver Real Results
Marketing in the B2B world isn’t about flashy ads or viral trends. It’s about building credibility, demonstrating expertise, and nurturing relationships over time. The most effective B2B marketing strategies combine content, data, and technology.
Content Marketing and Thought Leadership
High-quality content positions a company as an industry authority. Whitepapers, case studies, research reports, and blog posts educate prospects and guide them through the buyer’s journey.
- Content should address specific pain points and offer actionable solutions.
- SEO-optimized articles improve visibility and attract organic traffic.
- Webinars and podcasts engage audiences with real-time interaction.
For example, HubSpot’s blog generates millions of visits monthly by offering free, valuable marketing advice. This builds trust and converts readers into leads.
Email Marketing and Lead Nurturing
Email remains one of the most effective B2B marketing channels. Automated drip campaigns nurture leads by delivering relevant content based on behavior and stage in the sales funnel.
- Segmentation ensures messages are personalized and timely.
- Drip sequences guide prospects from awareness to consideration to decision.
- A/B testing improves open rates, click-throughs, and conversions.
According to Campaign Monitor, email delivers an average ROI of $42 for every $1 spent in B2B marketing.
Account-Based Marketing (ABM)
ABM is a strategic approach where marketing and sales teams collaborate to target high-value accounts with personalized campaigns.
- Instead of casting a wide net, ABM focuses on a select few companies.
- Customized content, ads, and outreach increase engagement.
- Success is measured by account engagement and revenue, not just leads.
Companies like Adobe and Salesforce use ABM to win enterprise clients. Research by ABM Institute shows that 87% of marketers report higher ROI from ABM than other marketing strategies.
The Role of Technology in Modern B2B Operations
Technology is the backbone of today’s B2B ecosystem. From automation to artificial intelligence, digital tools are transforming how companies sell, market, and serve their clients.
CRM and Sales Automation
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems like Salesforce, Zoho, and Microsoft Dynamics centralize customer data, track interactions, and streamline sales processes.
- CRMs provide a 360-degree view of the customer journey.
- Automation reduces manual tasks like data entry and follow-up emails.
- Analytics help forecast sales and identify bottlenecks.
With AI-powered insights, CRMs can now predict which leads are most likely to convert, enabling smarter prioritization.
Marketing Technology (MarTech) Stack
B2B companies rely on a suite of marketing technologies to execute campaigns efficiently. This includes email platforms, SEO tools, social media schedulers, and analytics dashboards.
- Hootsuite and Buffer manage social media outreach.
- SEMrush and Ahrefs optimize content for search engines.
- Google Analytics tracks user behavior and campaign performance.
The average B2B company uses over 10 MarTech tools, according to ChiefMartec’s 2023 landscape report.
AI and Data Analytics in B2B
Artificial intelligence is no longer futuristic—it’s a daily tool in B2B operations. AI powers chatbots, predicts customer churn, personalizes content, and even writes sales emails.
- Tools like Drift and Intercom use AI to qualify leads in real time.
- Predictive analytics identify which accounts are ready to buy.
- Natural language processing (NLP) analyzes customer feedback and support tickets.
According to PwC, AI could contribute up to $15.7 trillion to the global economy by 2030, with B2B sectors leading adoption.
Challenges and Solutions in the B2B Landscape
Despite its growth and potential, B2B commerce faces several challenges. From long sales cycles to intense competition, companies must adapt to stay ahead.
Long Sales Cycles and Decision Fatigue
One of the biggest hurdles in B2B is the extended sales cycle. With multiple stakeholders involved, approvals can take weeks or months.
- Solution: Streamline communication with clear timelines and decision trees.
- Provide decision-makers with all necessary information upfront.
- Use collaboration tools like Notion or Asana to keep everyone aligned.
Speed and clarity can significantly shorten the path to purchase.
Intense Competition and Market Saturation
Many B2B markets are crowded, especially in tech and SaaS. Standing out requires more than just a good product—it demands a strong brand and unique value proposition.
- Solution: Focus on niche markets or underserved industries.
- Highlight customer success stories and measurable results.
- Invest in thought leadership to differentiate from competitors.
As Harvard Business Review notes, differentiation through insight is more powerful than product features alone.
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
B2B companies handle sensitive business data, making cybersecurity a top priority. Breaches can damage trust and lead to legal consequences.
- Solution: Implement robust data encryption and access controls.
- Comply with regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
- Regularly audit systems and conduct employee training.
Transparency about security practices builds confidence among enterprise clients.
The Future of B2B: Trends Shaping the Next Decade
The B2B world is evolving rapidly. Emerging technologies, shifting buyer behaviors, and global economic changes are redefining how businesses interact and transact.
Rise of Self-Service and Digital Buying
Modern B2B buyers expect the same convenience as B2C shoppers. They want to research, compare, and purchase online without speaking to a sales rep.
- Companies are investing in e-commerce platforms with real-time pricing.
- Interactive product demos and AI chatbots enhance the buying experience.
- Transparent reviews and peer recommendations influence decisions.
A McKinsey study found that 74% of B2B buyers prefer remote or self-serve interactions.
Hyper-Personalization Through AI
Generic messaging no longer works. Buyers expect content and offers tailored to their industry, role, and challenges.
- AI analyzes behavioral data to deliver personalized website experiences.
- Dynamic content changes based on the visitor’s company size or location.
- Recommendation engines suggest relevant products or services.
Personalization can increase conversion rates by up to 20%, according to Salesforce.
Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing
More B2B buyers are prioritizing sustainability. They want suppliers who align with environmental and social values.
- Companies are adopting green manufacturing and carbon-neutral shipping.
- Transparency in supply chains is becoming a competitive advantage.
- ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) reporting is gaining traction.
A 2023 IBM report revealed that 68% of B2B procurement officers consider sustainability when choosing vendors.
What is B2B?
B2B, or business-to-business, refers to transactions where one company sells products or services to another company, rather than to individual consumers. It’s common in industries like manufacturing, software, and professional services.
How does B2B differ from B2C?
B2B involves longer sales cycles, multiple decision-makers, and a focus on ROI and efficiency. B2C is typically faster, emotionally driven, and targets individual consumers.
What are the most effective B2B marketing strategies?
Top strategies include content marketing, account-based marketing (ABM), email nurturing, and leveraging SEO and social media to build authority and generate leads.
Why is technology important in B2B?
Technology enables automation, data analytics, AI-driven insights, and seamless customer experiences. Tools like CRM, marketing automation, and e-commerce platforms are essential for scaling B2B operations.
What are the biggest challenges in B2B sales?
Common challenges include long sales cycles, intense competition, data security concerns, and the need for personalized, value-driven communication.
The B2B landscape is dynamic, complex, and full of opportunity. From its foundational principles to cutting-edge digital transformations, understanding B2B is essential for any business aiming to thrive in today’s interconnected economy. By mastering sales processes, leveraging technology, and adapting to emerging trends, companies can build lasting partnerships and drive sustainable growth. The future of B2B isn’t just about selling—it’s about solving, innovating, and leading with purpose.
Further Reading: