B2B2C Explained: 7 Powerful Insights You Need to Know
Ever heard of B2B2C but not quite sure what it means? You’re not alone. This evolving business model is quietly reshaping how companies connect with end consumers through strategic partnerships. Let’s break it down in simple, powerful terms.
What Is B2B2C? A Clear Definition

The term b2b2c—short for Business-to-Business-to-Consumer—refers to a model where one business sells its products or services to another business, which then delivers them to the end consumer. It’s a hybrid approach that combines the strengths of B2B efficiency and B2C customer engagement.
The Core Structure of B2B2C
At its heart, b2b2c involves three key players: the original product or service provider (B), the intermediary business (B), and the final customer (C). This structure allows companies to scale without directly managing consumer relationships.
- The first ‘B’ creates value (e.g., a software developer).
- The second ‘B’ distributes or enhances that value (e.g., a retailer or platform).
- The ‘C’ receives the final product or service (the end user).
“B2B2C isn’t just a sales model—it’s a strategic alliance that amplifies reach and deepens customer trust.” — Harvard Business Review
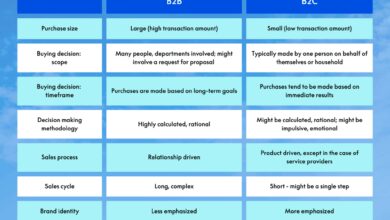
How B2B2C Differs from B2B and B2C
Unlike pure B2B, where transactions end at the business level, b2b2c extends the value chain all the way to the consumer. And unlike traditional B2C, the brand may not interact directly with the customer.
- B2B: Focuses on business needs, long sales cycles, bulk orders.
- B2C: Direct-to-consumer, emotional appeal, fast decisions.
- B2B2C: Blends both—strategic partnerships with consumer impact.
This hybrid model enables companies to leverage another brand’s customer base while maintaining product control.
The Rise of the B2B2C Model in Modern Commerce
The digital age has accelerated the adoption of b2b2c strategies. As markets become more interconnected, businesses are seeking smarter ways to expand their footprint without the overhead of direct consumer marketing.
Market Forces Driving B2B2C Adoption
Several trends have made b2b2c not just viable, but essential for growth-oriented companies:
- Digital platforms: Marketplaces like Amazon, Shopify, and Salesforce enable seamless integration between suppliers and retailers.
- Consumer demand for personalization: End users expect tailored experiences, which b2b2c models can deliver through data-sharing partnerships.
- Supply chain complexity: Companies outsource distribution to focus on innovation and core competencies.
According to a McKinsey report, over 60% of B2B companies are now exploring b2b2c models to enhance customer engagement.
Case Study: How Adobe Uses B2B2C
Adobe doesn’t sell Creative Cloud directly to every school or small business. Instead, it partners with authorized resellers and educational institutions (the second B), who then offer Adobe tools to students and professionals (the C).
- Adobe maintains brand control and pricing.
- Resellers handle onboarding and support.
- End users get localized, trusted service.
This model has helped Adobe scale globally while reducing customer acquisition costs.
Key Benefits of the B2B2C Business Model
Adopting a b2b2c strategy isn’t just about distribution—it’s about strategic advantage. Companies that master this model often outperform their peers in growth and customer loyalty.
Expanded Market Reach Without Direct Investment
One of the biggest advantages of b2b2c is the ability to enter new markets through established partners. Instead of building a sales team in every region, a company can collaborate with local distributors who already have customer trust.
- Reduced need for physical presence.
- Faster time-to-market.
- Lower marketing and logistics costs.
For example, IBM’s partnership with local tech integrators allows it to serve SMEs worldwide without direct engagement.
Enhanced Customer Experience Through Trusted Intermediaries
Consumers often trust local brands more than global corporations. In a b2b2c setup, the intermediary acts as a trusted advisor, improving adoption rates.
- Personalized onboarding and support.
- Cultural and language alignment.
- Higher perceived reliability.
“The intermediary isn’t just a middleman—it’s a relationship builder.” — Forbes
This is especially true in industries like healthcare, education, and fintech, where trust is paramount.
Data Sharing and Co-Created Value
B2B2C partnerships often involve shared data ecosystems. The original provider gains insights into end-user behavior, while the intermediary gets tools to improve service.
- Real-time usage analytics.
- Feedback loops for product improvement.
- Joint marketing campaigns based on shared KPIs.
For instance, SaaS companies like HubSpot share dashboard access with their agency partners, enabling co-management of client accounts.
Challenges and Risks in B2B2C Models
While the benefits are compelling, the b2b2c model isn’t without its pitfalls. Misalignment between partners can lead to brand dilution, customer confusion, or data conflicts.
Brand Control and Consistency Issues
When a third party represents your brand, maintaining consistent messaging and quality becomes challenging.
- Inconsistent customer service standards.
- Off-brand marketing materials.
- Misrepresentation of product capabilities.
To mitigate this, companies must establish clear brand guidelines and conduct regular audits of partner performance.
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
Sharing customer data across organizations increases the risk of breaches or misuse. GDPR, CCPA, and other regulations require strict compliance.
- Define data ownership and usage rights in contracts.
- Implement secure APIs and encryption protocols.
- Train partners on data handling best practices.
A Gartner study found that 43% of b2b2c failures stem from poor data governance.
Conflict of Interest Between Partners
Sometimes, the intermediary may promote competing products or prioritize their own offerings over yours.
- Lack of exclusivity agreements.
- Unclear revenue-sharing models.
- Differing customer retention goals.
Solution: Use performance-based incentives and tiered partnership programs to align interests.
Real-World Examples of Successful B2B2C Strategies
Theoretical understanding is one thing, but seeing b2b2c in action makes it tangible. Let’s explore how leading companies have leveraged this model to dominate their markets.
Microsoft and Its Global Partner Network
Microsoft doesn’t sell Azure or Microsoft 365 directly to every business. Instead, it relies on a vast network of certified partners—from IT consultants to system integrators—who implement, support, and upsell Microsoft solutions.
- Partners earn commissions and certifications.
- Microsoft gains deeper market penetration.
- End customers receive hands-on support.
This ecosystem has helped Microsoft become a leader in cloud services, with partners driving over 90% of its commercial sales.
Stripe and Embedded Finance
Stripe enables platforms like Shopify, Slack, and Uber to offer financial services (e.g., payouts, invoicing) under their own brand. Stripe is the backend provider (first B), the platform is the distributor (second B), and the merchant or user is the consumer (C).
- Stripe handles compliance and infrastructure.
- Platforms enhance their value proposition.
- End users enjoy seamless financial tools.
This b2b2c model has made Stripe a $50B+ company without a direct consumer brand.
John Deere and Agricultural Retailers
John Deere manufactures high-tech farming equipment, but it doesn’t sell directly to every farmer. Instead, it works with local agricultural dealers who sell, service, and finance the machinery.
- Dealers provide training and maintenance.
- John Deere focuses on R&D and innovation.
- Farmers get localized, expert support.
This model strengthens customer loyalty and ensures long-term equipment performance.
How to Build a Winning B2B2C Strategy
Transitioning to a b2b2c model requires more than just finding a partner. It demands a strategic framework that aligns goals, technology, and customer experience.
Step 1: Identify the Right Partners
Not all businesses make good intermediaries. Look for partners who:
- Share your brand values.
- Have an established customer base.
- Offer complementary services.
Use a scoring matrix to evaluate potential partners on reach, reliability, and technical capability.
Step 2: Align Incentives and KPIs
Ensure both parties benefit. Common alignment tools include:
- Revenue-sharing agreements.
- Performance bonuses.
- Co-branded marketing budgets.
Regular joint reviews help maintain alignment and address issues early.
Step 3: Integrate Technology and Data Systems
Seamless integration is critical. Use APIs, partner portals, and shared dashboards to enable real-time collaboration.
- Automate order and inventory tracking.
- Enable single sign-on for partner access.
- Provide self-service training and support.
Tools like Salesforce Partner Cloud or PartnerStack can streamline this process.
The Future of B2B2C: Trends to Watch
The b2b2c model is evolving rapidly. As technology advances and consumer expectations shift, new opportunities are emerging for forward-thinking companies.
The Rise of Embedded Commerce
More businesses are embedding products and services into third-party platforms. For example, insurance providers now offer policies directly within car leasing apps.
- Frictionless customer journeys.
- Higher conversion rates.
- New revenue streams.
This trend is expected to grow as APIs and microservices become more accessible.
AI-Powered Partner Management
Artificial intelligence is being used to optimize partner selection, predict performance, and personalize support.
- AI-driven matchmaking between suppliers and distributors.
- Predictive analytics for churn risk.
- Chatbots for partner onboarding.
Companies like SAP and Oracle are already integrating AI into their partner ecosystems.
Sustainability and Ethical B2B2C Partnerships
Consumers are increasingly concerned about sustainability. B2B2C models allow brands to extend their ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) values through partners.
- Green logistics partnerships.
- Ethical sourcing certifications.
- Transparency in supply chains.
A PwC report shows that 78% of consumers prefer brands that partner with eco-conscious distributors.
What is the main advantage of a b2b2c model?
The main advantage of a b2b2c model is the ability to scale market reach and enhance customer experience through trusted intermediaries, without the high costs of direct consumer engagement. It combines B2B efficiency with B2C impact.
How does b2b2c differ from traditional B2B?
Unlike traditional B2B, which ends the transaction at the business level, b2b2c extends the relationship to the end consumer. It involves shared branding, customer experience, and often data collaboration between the original provider and the intermediary.
Can small businesses use b2b2c strategies?
Absolutely. Small businesses can partner with larger platforms or local distributors to access new markets. For example, a boutique software developer can sell through a SaaS marketplace, leveraging the platform’s customer base and infrastructure.
What industries benefit most from b2b2c?
Industries that benefit most include technology (SaaS, cloud services), healthcare (telemedicine platforms), education (e-learning tools), finance (embedded banking), and manufacturing (equipment distribution).
How do you measure success in a b2b2c partnership?
Success can be measured through joint KPIs such as customer acquisition cost (CAC), lifetime value (LTV), partner sales volume, customer satisfaction (CSAT), and data-sharing compliance rates.
The b2b2c model is more than a trend—it’s a strategic evolution in how value is delivered. By combining the strengths of business partnerships with direct consumer impact, companies can achieve scalable growth, deeper customer relationships, and sustainable competitive advantage. Whether you’re a startup or an enterprise, understanding and leveraging b2b2c could be your next big leap forward.
Further Reading: